Geozones introduction
What are geozones and geozone visits? What value does the geozone functionality provide?
What is a geozone?
A geozone (or geographical zone) is a geographical boundary that defines an area of interest such as a warehouse or parking lot. Once defined it allows to get insights regarding stock levels, stay times, in-and-out flows and much more. Geozones are used to group raw location data points and translate this into recognizable locations, and to provide context and meaning to asset localization. For example, a geozone can be used to count all assets in a specific warehouse location.
Knowing how to manage geozones is important, because geozones are used in several advanced functionalities in the platform, such as geozone-based alert rules, geozone reports and geozone stock levels.
In this tutorial a good introduction to geozones is presented.
Using geozones brings value for monitoring and optimizing different business processes:
- Get automated inventory levels, avoiding manual inventory counting.
- Verify that the loading/unloading time in a specific geozone was within agreed limits.
- Get notified when assets are entering or leaving a geozone.
- Follow up and get notified when stock levels are too low/high.
- Know if your assets are being returned on time.
- Learn about the rotation time of your assets.
What is a geozone visit?
A geozone visit refers to stay of an asset has in a specific geozone. The duration of the stay is defined by the captured arrival and departure time. Geozone visits allow to get insights in for example the average time assets stay in a specific geozone or in assets staying to long in a specific geozone.
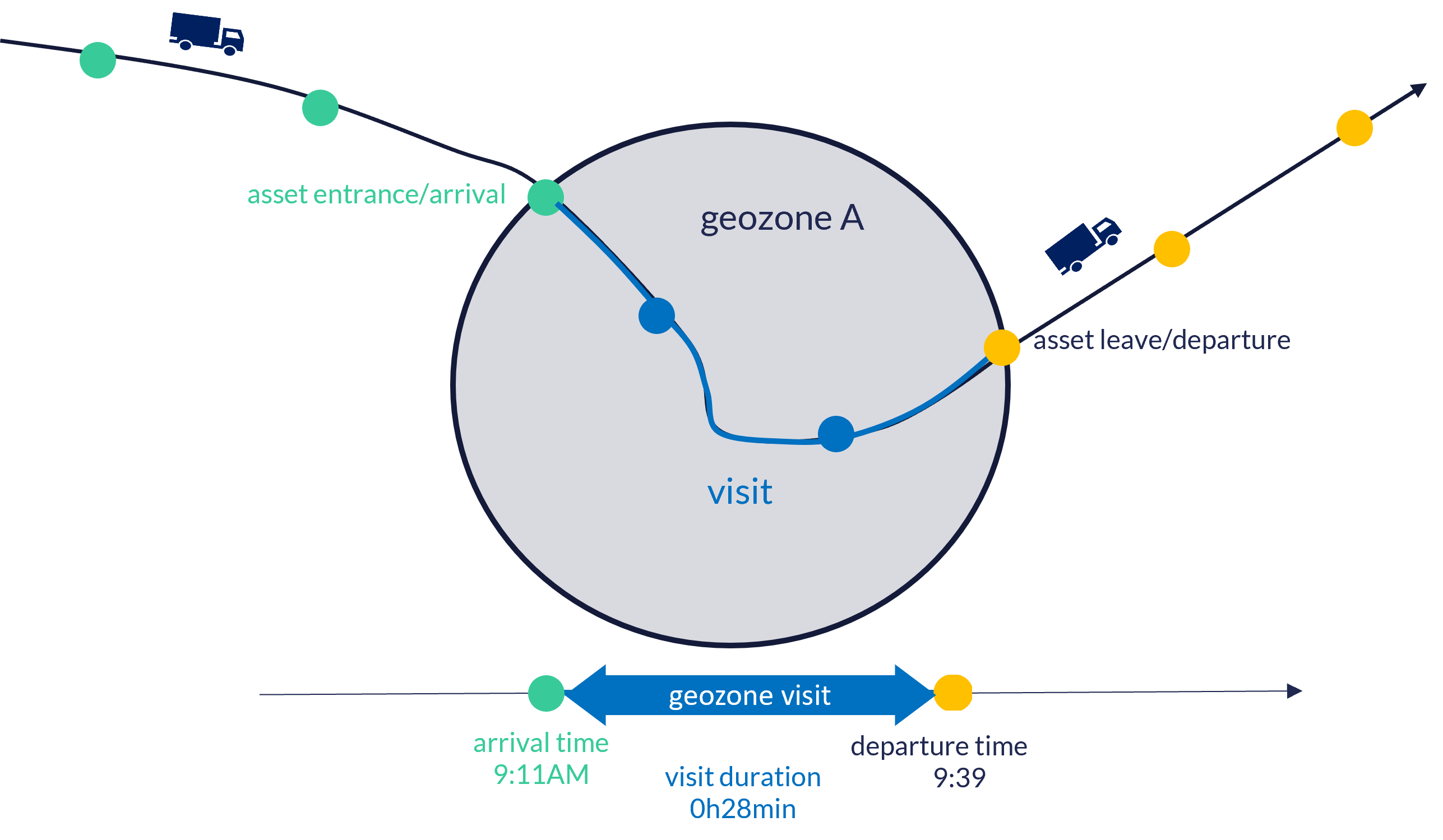
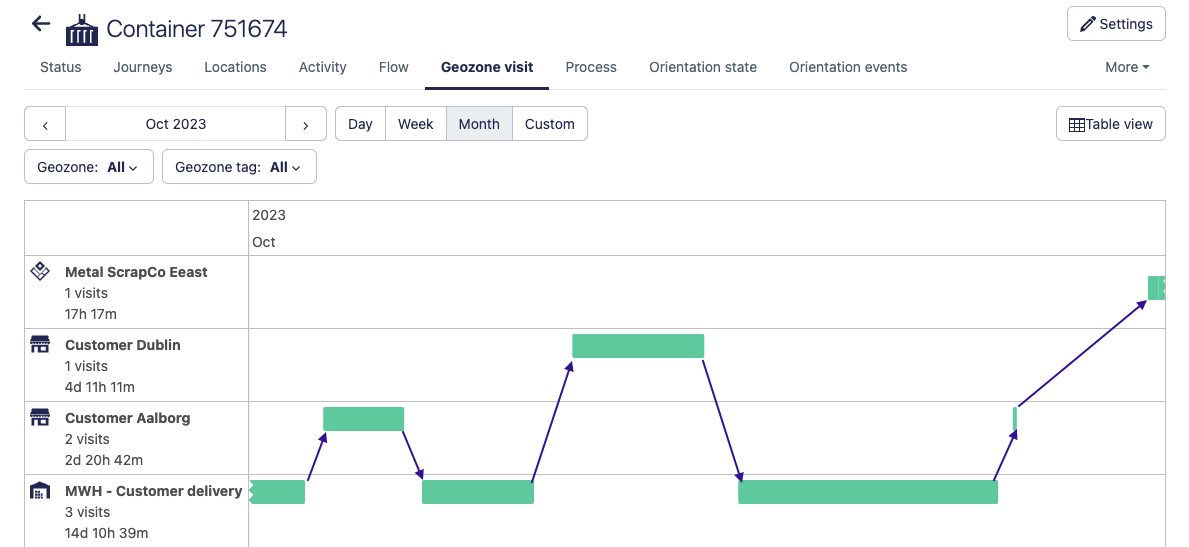
When an asset travels to different locations for which different geozones have been created, the geozone visit functionality provides a clear overview to users, without needing to navigate a map and look up individual location points. This is demonstrated the following image, which shows the timeline view for an individual asset that has moved between different geozones:
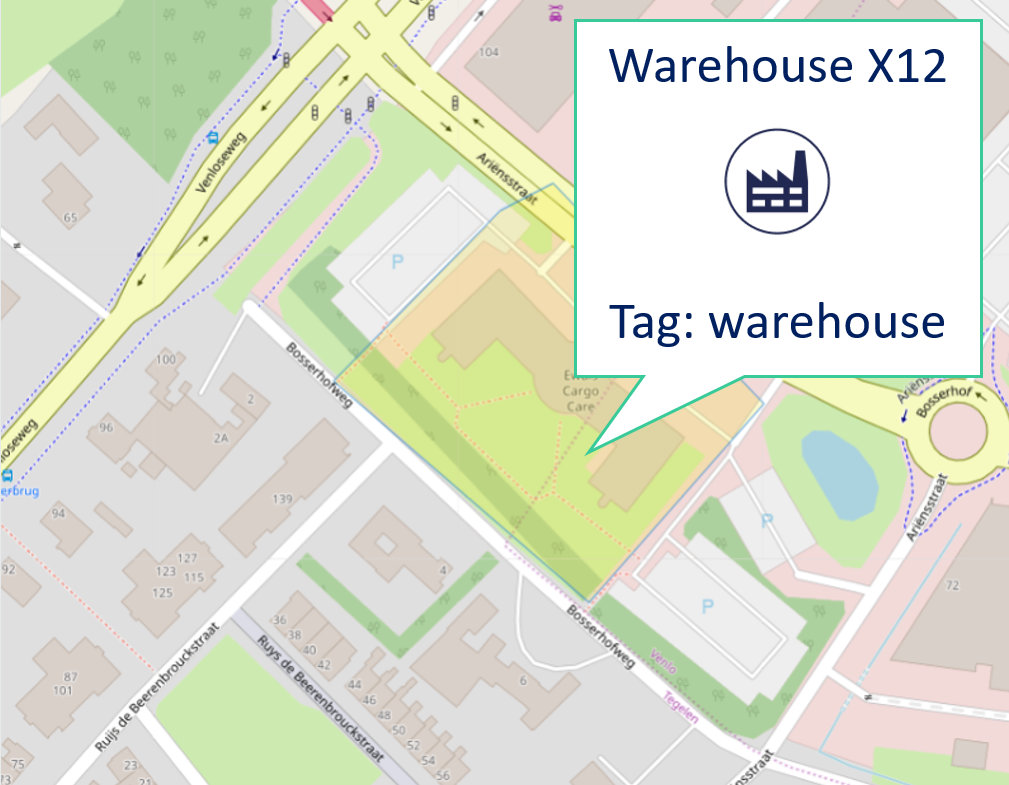
What is a geozone tag?
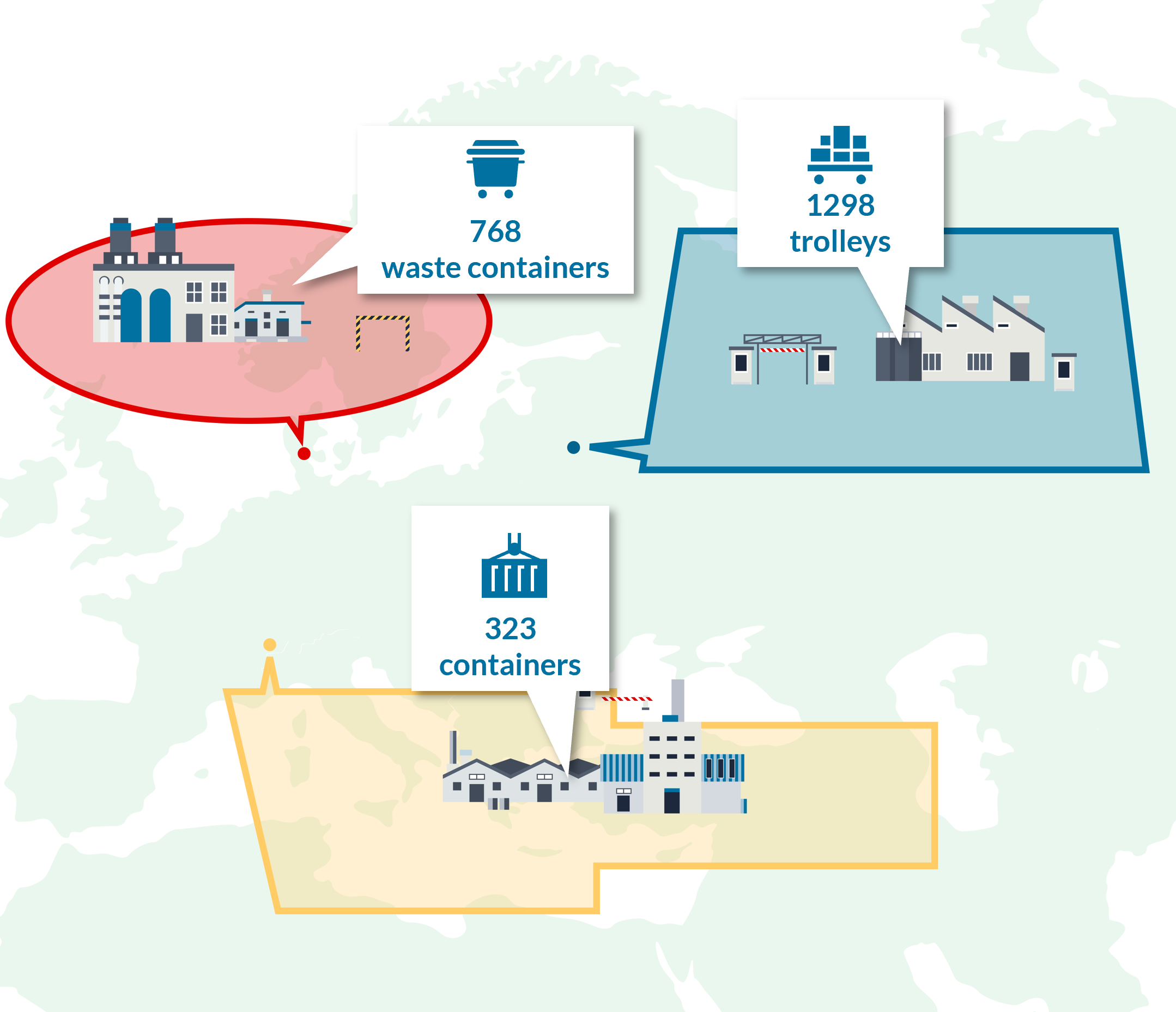
A geozone tag is a label that can be assigned to geozones in order to group them and assign meaningful context.. Examples of commonly used geozone tags are 'warehouse', 'supplier', 'customer', 'parking','country'... Geozone tags can be used to filter lists and drill down dashboard views. For example, geozone tags can be used to count all assets inside all warehouses (= sum of all assets in geozones tagged with 'warehouse').
Geozone tags have multiple purposes:
- Geozone tags provide more information and context for end-users interacting with the geozone, in addition to the geozone name. For example, you can tag geozones as a 'factory', 'storage yard', 'warehouse'.
- Geozone tags make it easier for administrators to manage a large number of geozones by filtering on geozone tags.
- The Sensolus platform provides several advanced functionalities that operate on groups of geozones, identified by geozone tags
Geozone shape
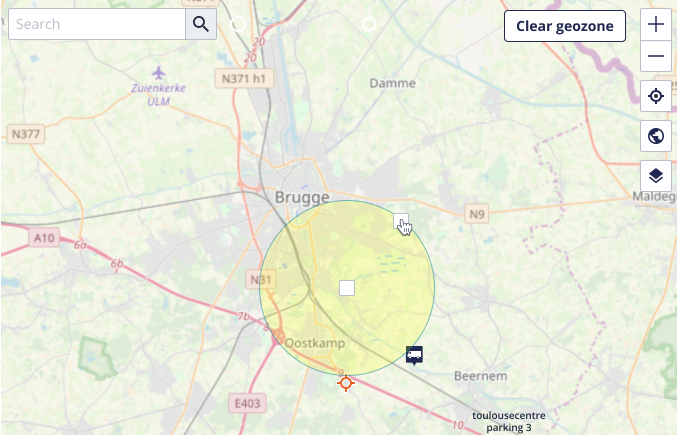
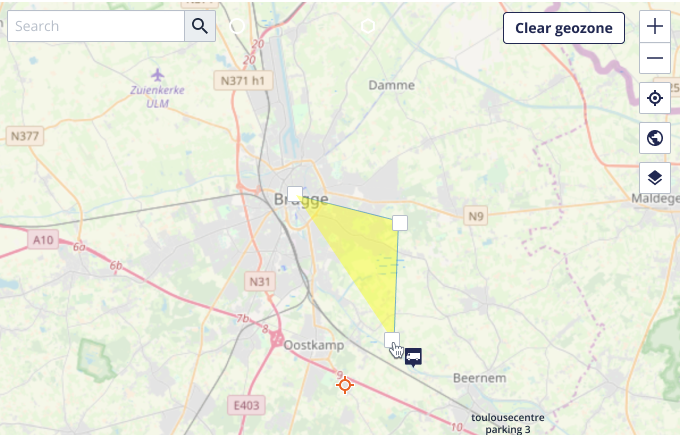
A geozone is defined as either a circle or a polygon, located on a map.
- Circle: A circular geozone has a center location, and a radius attribute. Due to its simplicity, circular geozones are easy to create, resize and move.
- Polygon: The shape of a polygonal geozone is defined by a sequence of locations points. A polygonal geozone is more flexible than a circular geozone, however it may take a bit longer to enter all the location points.